Don’t hesitate to contact us:
Forum: discuss.graphhopper.com
Email: support@graphhopper.com
A map matching software makes your recorded GPS points ‘snap’ to some digital road network. E.g. the open source map matching component from GraphHopper is a highly customizable solution also available as SaaS. The following picture illustrates this map matching process from recorded data (blue) to matching data (green):
But why is this ‘snap to road’ useful? For that we will look today into three possible usage scenarios. Before we start we need to clarify the wording a bit. A GPS point is a location on earth with latitude and longitude data, and a GPX point is a GPS point with an associated timestamp. So when you record your walking or biking trail you often have a GPX file which is a list of GPX points.
The Google Maps Roads API allows you to make GPX tracks align to their proprietary road network, which is useful. They also allow you to attach the maximum allowed speed but no further information and only for business customers. A solution like a map matching component from GraphHopper which is based on OpenStreetMap has some advantages over that:

Attach any OpenStreetMap way tag to the GPX track like maxspeed=50 in this example.
If you track vehicles the data will suffer from GPS device precision errors, which also means that the speed and location is not that exact. Having more precise road network data and use this to enhance your recorded data will help you to calculate more precise distance and speed values for your tracked vehicles.
Once you have recorded the GPX tracks and transformed them into digital paths you know the road IDs. With that information you can easily detect if two vehicles are passing the same road although the GPS coordinates are completely different and just ‘similar’ in location. This makes it easier to assign values like the measured speed to a road. Also this data can be used for traffic influenced routing.
Furthermore an open source solution makes it easy to
Have fun when playing around and let us know about your use case!
Nearly all electric vehicles to date that rely 100% on electric energy have a range problem, especially in cold seasons. The only exceptions are maybe Tesla and fuel cell driven cars with over 400km and some even over 500km range. If you still want to plan a longer-distance tour you’ll have to include one (or more) charging station as stopover.
But how to find the best one with the least detour e.g. in this example from Hamburg to Munich?
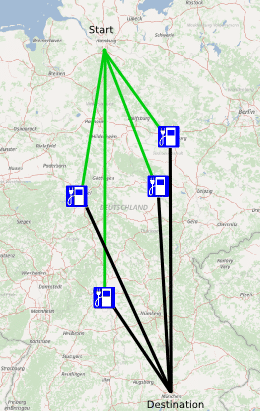
You calculate all routes to all charging stations and pick the best. That sounds crazy but is completely reasonable in real time with GraphHopper even for hundreds of stations. In this blog post we’ll use the GraphHopper Matrix API and have created the JavaScript charging station example.
The GraphHopper Matrix API is a specially crafted piece of software to make many-to-many requests very fast. For example in logistics you need this to determine the optimal order for e.g. delivering parcels.
Now to calculate the best detour we need a similar logic: we need
A) one request, the one-to-many and
B) another request, the many-to-one.
Finally we’ll pick the fastest tour (smallest A+B). The same approach we would take to calculate an optimal ridesharing where you ‘pick up’ and ‘deliver’ people.
We also need all charging stations and grab them from OpenStreetMap via the Overpass API and use the wizard to specify amenity=charging_station and car=yes. We ignore for a moment the socket type of the station and a possible required authentication or fee.
For the German tour from Hamburg to Munich we fetch all stations from middle Germany (roughly 80) and select all which are in the center of our route e.g. within a 400km radius (reducing this is necessary for the free package).
There are several optimizations possible like the route calculating itself to consider elevation to avoid hills or a completely other vehicle like an electric bicycle. Or in real world you have to consider the opening hours of the stations or seek for multiple stops for shorter ranges, then the Tour Optimization API or special routing expertise could be necessary.
In our Hamburg-Munich case the result is the following tour of ~750km and roughly 8.5 hours plus the time required for charging or replacing the battery at this charging station in Erfurt. Compare this to the normal route which takes only 8 hours and is 775km long.
